|
|
| (267 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) |
| Line 1: |
Line 1: |
| | __NOTOC__ | | __NOTOC__ |
| − | The ''Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)'' was created by the '''Body of Knowledge and Curriculum to Advance Systems Engineering ([http://www.bkcase.org BKCASE])''' project.
| |
| | | | |
| − | [[Systems Engineering (glossary)|Systems engineering]] is an interdisciplinary approach and means to enable the full life cycle of successful systems, including problem formulation, solution development and operational sustainment and use. Those new to Systems Engineering can find introductory articles which provide an [[Systems Engineering Overview|overview of systems engineering]], place it in [[Systems Engineering: Historic and Future Challenges|historical context]], and discuss its [[Economic Value of Systems Engineering|economic value]] in [[SEBoK Introduction|Part 1]] of this body of knowledge. | + | <center>'''On behalf of the [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board#Editorial Board|Editorial Board]]<nowiki/>, the [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board#BKCASE Governing Board|Governing Board]], and our authors and sponsors, welcome to |
| | | | |
| − | The BKCASE Project began in the fall of 2009. Its aim was to add to the professional practice of systems engineering by creating two closely related products:
| + | '''SEBoK version 2.9.'''</center> |
| − | *''Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)''
| + | <center>Released 20 November 2023</center> |
| − | *''Graduate Reference Curriculum for Systems Engineering (GRCSE)''
| |
| | | | |
| − | The SEBoK came into being out of a recognition that the systems engineering discipline could benefit greatly by having a living authoritative guide closely related to those groups developing guidance on advancing the practice, education, research, work force development, professional certification, standards, etc. | + | == Welcome to SEBoK v. 2.9 == |
| | + | <div style="text-align:justify"> |
| | + | The SEBoK provides a guide to the [[Primary References|key knowledge sources and references]] of {{Term|Systems Engineering (glossary)|systems engineering}} organized and explained to assist a wide variety of individuals. It is a living product, accepting community input continuously, with regular refreshes and updates. The SEBoK is not a compendium but instead references existing literature. |
| | | | |
| − | At the beginning of 2013, BKCASE transitioned to a new governance model with shared stewardship between the [http://www.sercuarc.org Systems Engineering Research Center (SERC)], the [http://www.incose.org International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE)], and the [http://www.computer.org Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Computer Society (IEEE-CS)]. This governance structure was formalized in a memorandum of understanding between the three stewards that was finalized in spring of 2013. The stewards have reconfirmed their commitment to making the SEBoK available at no cost to all users, a key principle of BKCASE.
| + | '''Systems engineering''' is an interdisciplinary approach and means to enable the full life cycle of successful {{Term|Product System (glossary)|product}}, {{Term|Service_System_(glossary)|service}} and {{Term|Enterprise_System_(glossary)|enterprise}} systems. It includes problem discovery and formulation, solution definition and realization, and operational use, sustainment, and disposal. It can be applied to single-problem situations or to the management of multiple interventions in commercial or public enterprises. Those new to systems engineering can find introductory articles which provide an [[Systems Engineering Overview|overview of systems engineering]], place it in [[Systems Engineering: Historic and Future Challenges|historical context]], and discuss its [[Economic Value of Systems Engineering|economic value]] in [[SEBoK Introduction|Part 1]] of this body of knowledge.</div> |
| | | | |
| − | Please see http://www.bkcase.org for more information.
| + | ==What's New?== |
| | + | [[File:DownloadtheSEBoK.png|200px|right|link={{filepath:Guide_to_the_Systems_Engineering_Body_of_Knowledge_v2.9.pdf}}]] |
| | + | A few things to look forward to in the latest update: |
| | + | *[[Governance and Editorial Boards]] changes including a new Editor-in-Chief and Managing Editor |
| | + | *A new article on [[Reverse Engineering a UAV Prototype using Agile Practices]] |
| | + | *A new article on [[System Security]] that replaces the one found in SEBoK 2.8 |
| | + | *A new article on the [[An Overview of the SWEBOK Guide]] that replaces the one found in SEBoK 2.8 |
| | + | *An updated article on Loss Driven Systems Engineering, [[A Framework for Viewing Quality Attributes from the Lens of Loss]] |
| | + | *An updated article on [[System Resilience]] |
| | + | *A transition from the use cases originally published in SEBoK v. 1.0 to more persona-driven guidance for different types of [[SEBoK Users and Uses|users]] |
| | + | *Minor updates to articles throughout the SEBoK |
| | | | |
| − | ==Welcome to SEBoK v. 1.3.1== | + | ==SEBoK Organization== |
| − | On behalf of the [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board|BKCASE Editorial Board]] and the three [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board#BKCASE Governing Board|SEBoK steward organizations]], welcome to SEBoK v. 1.3.1.
| |
| | | | |
| − | The SEBoK provides a compendium of the [[Primary References|key knowledge sources and references]] of systems engineering that are organized and explained to assist a wide variety of [[SEBoK Users and Uses|users]]. It is a living product, accepting community input continuously, with regular refreshes and updates.
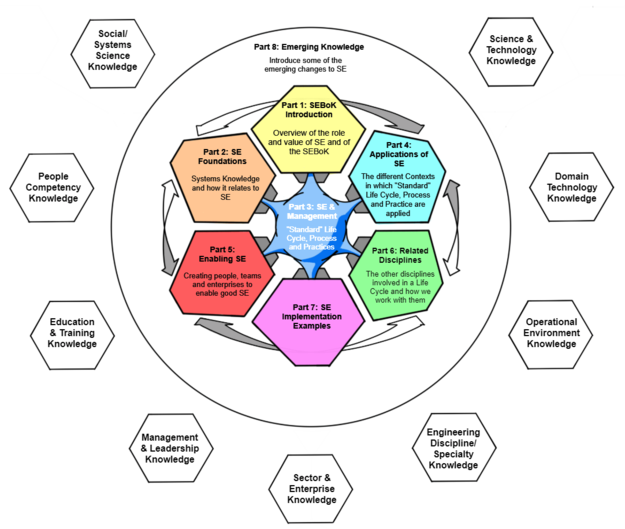
| + | {{Structure|625px|'''Figure 1. Scope of SEBoK: Parts and related knowledge.''' Click on a Part to navigate to it. (SEBoK Original).|right}} |
| | | | |
| − | This version was released 5 December 2014, and contains a number of minor updates to references and text. There is no significant change to SEBoK content for this update. For a summary of the changes made for v. 1.3.1 see the [[Letter from the Editor]]. See [[Acknowledgements and Release History]] for a full description of the current and all previous SEBoK versions.
| + | The SEBoK is a '''guide''' to the broad scope of SE-related knowledge. The core of this is tested and proven knowledge that has been developed through practice, documented, reviewed, and discussed by the SE community. In addition, the SEBoK also covers some of the emerging aspects of SE practice, such as Systems of Systems, Agile Life Cycle approaches and Model Based Systems Engineering (MBSE). |
| | | | |
| − | ==BKCASE History, Motivation, and Value==
| + | Systems engineering has its roots in the fundamentals, principles, and models of foundational systems sciences, and associated management and engineering sciences. It is effective systems engineering processes are applied within a managed life cycle working with a number of other management, engineering, and specialist disciplines. While traditionally applied to product development, systems engineering can also be applied to {{Term|Service_System_(glossary)|service}} and {{Term|Enterprise_System_(glossary)|enterprise}} systems. As systems engineering is a collaborative approach, working with other engineering and management disciplines and specialties, it relies on competencies at the individual and team levels and appropriate structure and governance at organizational levels. |
| | | | |
| − | The '''Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK)''' is a living authoritative guide that discusses what is included in the discipline, how the discipline should be structured to facilitate understanding, and what documents are the most important to the discipline. The curriculum guidance in the '''Graduate Reference Curriculum for Systems Engineering (GRCSE)''' (Pyster and Olwell et al. 2012) makes reference to sections of the SEBoK to define its core knowledge; it also suggests broader program outcomes and objectives which reflect aspects of the professional practice of systems engineering as discussed across the SEBoK.
| + | Starting from this basic view of the scope of knowledge relevant to SE, the SEBoK is organized into [[SEBoK Table of Contents|8 parts]] as shown in Figure 1. '''Click on Figure 1 to navigate to any part of the SEBoK.''' |
| | | | |
| − | Between 2009 and 2012 BKCASE was led by Stevens Institute of Technology and the Naval Postgraduate School in coordination with several professional societies and sponsored by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), which provided generous funding. More than 75 authors and many other reviewers and supporters from dozens of companies, universities, and professional societies across 10 countries contributed many thousands of hours writing the SEBoK articles; their organizations provided significant other contributions in-kind. For additional information on the BKCASE authors, please see the [[Acknowledgements and Release History]] article.
| + | The SEBoK includes a [[Glossary of Terms|glossary]] and a list of [[Primary References|recommended references]]. The main content of the SEBoK can be downloaded as a PDF for offline access if desired. |
| − | | |
| − | The first value of the BKCASE project has simply been the greater sense of community that has developed among the authors, which include many fellows of professional societies and other leaders in the field. For example, the relationship between Systems Science and Systems Engineering is now more clearly understood than in the past. This relationship is captured in Parts 2 and 3 of the SEBoK. | |
| − | | |
| − | The greater value of the SEBoK, of course, comes from use by the community. '''As of the end of Oct 2014, SEBoK articles have been accessed more than 450,000 times by over 120,000 users.''' We hope the SEBoK will regularly be used by thousands of systems engineers around the world as they undertake such activities as creating systems architectures, developing career paths for systems engineers, and deciding new curricula for systems engineering university programs, etc.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==About the SEBoK==
| |
| − | | |
| − | Systems engineering has its roots in the fundamentals, principles, and models of systems thinking. It is applied through the application of systems engineering processes within a managed life cycle working with a number of other management, engineering, and specialist disciplines. While traditionally applied to product development, systems engineering can also be applied to [[Service_System_(glossary)|service]] and [[Enterprise_System_(glossary)|enterprise]] systems. As systems engineering is a collaborative approach it relies on enabling competencies and structures at individual, team, and organizational levels.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The SEBoK is organized into [[SEBoK Table of Contents|7 parts]], with a [[Glossary of Terms]] and a list of [[Primary References]], to reflect the scope of Systems Engineering knowledge and its links into other bodies of knowledge.
| |
| − | | |
| − | * [[SEBoK Introduction|Part 1]] discusses the SEBoK's [[Scope of the SEBoK|scope]] and [[Structure of the SEBoK|structure]], including its hierarchy of parts, [[:Category:Knowledge_Area|knowledge areas]], and [[:Category:Topic|topics]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | The other parts include: | |
| − | * Part 2 [[Systems]]
| |
| − | * Part 3 [[Systems Engineering and Management]]
| |
| − | * Part 4 [[Applications of Systems Engineering]]
| |
| − | * Part 5 [[Enabling Systems Engineering]]
| |
| − | * Part 6 [[Related Disciplines]]
| |
| − | * Part 7 [[Systems Engineering Implementation Examples]]
| |
| − | | |
| − | Part 1 also includes a lengthy discussion of [[SEBoK Users and Uses]], including a number of [[:Category:Use_Case|use cases]] which give advice on how different groups of users might navigate and use the SEBoK. This is a good place to start if you are new to the SEBoK. Individuals who are new to systems engineering can start with [[Use Case 0: Systems Engineering Novices]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | Articles in the SEBoK can be found by using the ''Search'' field in the upper right corner of each page, as well as through the ''Quicklinks'', ''Outline'', and ''Navigation'' menus in the left margin of each page. Detailed instructions about the page layout and features are found in [[How to Read the SEBoK]]. There is a link in the left margin under ''Quicklinks'' explaining how to [[Cite the SEBoK]] correctly.
| |
| − | | |
| − | As a living document, at the bottom of each page, version identification can be found in a link called "[[About the SEBoK]]." A PDF of the SEBoK v. 1.3.1 - as well as archive copies of versions 1.0, 1.1, 1.2, and 1.3 - may be downloaded at [[Download SEBoK PDF]].
| |
| − | | |
| − | As the SEBoK is a compendium, much of the content has restricted intellectual property rights. This [[Bkcase Wiki:Copyright |copyright information]] is placed on each page, and must be respected. The SEBoK copyright is held by the Trustees of the Stevens Institute of Technology.
| |
| − | | |
| − | ==About SEBoK Updates and the Sandbox==
| |
| − | | |
| − | The SEBoK is sometimes compared to Wikipedia. The SEBoK is like Wikipedia in its most fundamental structure, as it is a collection of electronic articles built on MediaWiki technology. However, the SEBoK is unlike Wikipedia in that its content is carefully controlled. Anyone in the community can suggest changes be made to SEBoK articles, but the [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board#BKCASE Editorial Board|Editorial Board]] will review all recommendations before they are actually implemented in the SEBoK wiki.
| |
| − | | |
| − | New releases of the SEBoK are under the control of a [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board#BKCASE Governing Board|Governing Board]] appointed by the stewards, who oversee the SEBoK Editor in Chief and Editorial Board. The stewards contribute resources to manage the SEBoK wiki, support new releases, and encourage SEBoK adoption. Volunteer authors from the worldwide SE community continue to propose and create new content and other volunteers review that new content.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Wikipedia is a much more open wiki, allowing virtually anyone to change any article, while reserving the right to undo changes that are offensive or otherwise violate Wikipedia's rules. Tight control over SEBoK content is a trade-off. Such control ensures a stable baseline whose quality and integrity are assured by its editors. On the other hand, such control discourages some members of the community from contributing improvements to the SEBoK.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Comments can be left on any page of the current SEBoK version using the [http://help.disqus.com/ DISQUS] feature. These are periodically reviewed. Comments can be flagged in DISQUS, which will result in a faster review by the editors. You may also review the current [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board|Editorial Board]] and contact editors directly about the materials in their areas of responsibility.
| |
| − | | |
| − | To satisfy the need for a stable baseline and the desire for broader community involvement, the Editorial Board has implemented a collaborative space. The '''[[Sandbox|SEBoK Sandbox]]''' is a copy of the SEBoK that is separate from the baseline version where anyone in the community can edit articles, recommend new content, or provide comments on existing articles. It is important to note that while anyone in the community can gain access to the Sandbox, all submissions must still be approved by the Editorial Board before they will be folded into a new baseline version of the SEBoK. For more information on how this works, please '''[http://www.sebokwiki.org/sandbox visit the Sandbox]'''.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The Sandbox associated with v. 1.3.1 will open in January 2015, allowing the community to propose changes for v. 1.4, which is expected to be released in spring 2015.
| |
| − | | |
| − | The BKCASE Editorial Board uses the in line comments, collaboration via the sandbox and direct involvement with community groups and individuals to coordinate regular review and update of the SEBoK in a way which is both controlled and transparent. To find out more and to contact the editors please visit http://www.bkcase.org.
| |
| − | | |
| − | Email may be sent to [mailto:bkcase.incose.ieeecs@gmail.com bkcase.incose.ieeecs@gmail.com].
| |
| − | | |
| − | ----
| |
| − | | |
| − | <center>[[SEBoK Introduction|Go to Part 1 >]]</center>
| |
| | | | |
| | + | ==SEBoK Governance== |
| | + | The SEBoK is overseen by the [[BKCASE Governance and Editorial Board#BKCASE Governing Board|Governing Board]] appointed by the stewards, who oversee the SEBoK Editor-in-Chief and Editorial Board. The stewards contribute resources to manage the SEBoK wiki, support new releases, and encourage SEBoK adoption. Volunteer authors from the worldwide SE community continue to propose and create new content. Other volunteers review that new content. The stewards are INCOSE, the IEEE Systems Council, and Stevens Institute of Technology. |
| | | | |
| | <center> | | <center> |
| | {| | | {| |
| | + | |+ '''SEBoK Stewards''' |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |style="background-color: #ffffff"|[[File:INCOSE-logo-.jpg]] | + | | style="background-color: #ffffff" |[[File:INCOSE-logo-2016.jpg|250px|center|International Council on Systems Engineering|link=http://www.incose.org]] |
| − | |style="background-color: #ffffff"|[[File:CSlogo.png|350px|center|Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Computer Society]] | + | | style="background-color: #ffffff" |[[File:Ieee systems council logo.png|200px|center|Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Systems Council|link=https://ieeesystemscouncil.org/]] |
| | |- | | |- |
| − | |colspan="2" style="background-color: #ffffff"|[[File:SERC_logo.jpg|350px|center|Systems Engineering Research]] | + | | colspan="2" style="background-color: #ffffff" |[[File:Stevens-Official-PMSColor-R.png|350px|center|Stevens Institute of Technology|link=http://www.stevens.edu]] |
| | | | |
| | |} | | |} |
| | </center> | | </center> |
| | | | |
| | + | '''Contact us at [mailto:sebok@incose.net sebok@incose.net].''' |
| | + | |
| | + | ---- |
| | + | |
| | + | <center>[[SEBoK Introduction|Go to Part 1 >]]</center> |
| | | | |
| | + | {{#seo:description=The Guide to the Systems Engineering Body of Knowledge (SEBoK) is a living, authoritative guide of the Systems Engineering discipline. |
| | + | }} |
| | | | |
| − | {{DISQUS}}
| + | <center>'''SEBoK v. 2.9, released 20 November 2023'''</center> |
On behalf of the Editorial Board, the Governing Board, and our authors and sponsors, welcome to
SEBoK version 2.9.
Released 20 November 2023
Welcome to SEBoK v. 2.9
The SEBoK provides a guide to the key knowledge sources and references of systems engineeringsystems engineering organized and explained to assist a wide variety of individuals. It is a living product, accepting community input continuously, with regular refreshes and updates. The SEBoK is not a compendium but instead references existing literature.
Systems engineering is an interdisciplinary approach and means to enable the full life cycle of successful
productproduct,
serviceservice and
enterpriseenterprise systems. It includes problem discovery and formulation, solution definition and realization, and operational use, sustainment, and disposal. It can be applied to single-problem situations or to the management of multiple interventions in commercial or public enterprises. Those new to systems engineering can find introductory articles which provide an
overview of systems engineering, place it in
historical context, and discuss its
economic value in
Part 1 of this body of knowledge.
What's New?
A few things to look forward to in the latest update:
SEBoK Organization
Figure 1. Scope of SEBoK: Parts and related knowledge. Click on a Part to navigate to it. (SEBoK Original).
The SEBoK is a guide to the broad scope of SE-related knowledge. The core of this is tested and proven knowledge that has been developed through practice, documented, reviewed, and discussed by the SE community. In addition, the SEBoK also covers some of the emerging aspects of SE practice, such as Systems of Systems, Agile Life Cycle approaches and Model Based Systems Engineering (MBSE).
Systems engineering has its roots in the fundamentals, principles, and models of foundational systems sciences, and associated management and engineering sciences. It is effective systems engineering processes are applied within a managed life cycle working with a number of other management, engineering, and specialist disciplines. While traditionally applied to product development, systems engineering can also be applied to serviceservice and enterpriseenterprise systems. As systems engineering is a collaborative approach, working with other engineering and management disciplines and specialties, it relies on competencies at the individual and team levels and appropriate structure and governance at organizational levels.
Starting from this basic view of the scope of knowledge relevant to SE, the SEBoK is organized into 8 parts as shown in Figure 1. Click on Figure 1 to navigate to any part of the SEBoK.
The SEBoK includes a glossary and a list of recommended references. The main content of the SEBoK can be downloaded as a PDF for offline access if desired.
SEBoK Governance
The SEBoK is overseen by the Governing Board appointed by the stewards, who oversee the SEBoK Editor-in-Chief and Editorial Board. The stewards contribute resources to manage the SEBoK wiki, support new releases, and encourage SEBoK adoption. Volunteer authors from the worldwide SE community continue to propose and create new content. Other volunteers review that new content. The stewards are INCOSE, the IEEE Systems Council, and Stevens Institute of Technology.
Contact us at sebok@incose.net.
Go to Part 1 >
SEBoK v. 2.9, released 20 November 2023