Difference between revisions of "Types of Models"
m (Text replacement - "<center>'''SEBoK v. 2.0, released 1 June 2019'''</center>" to "<center>'''SEBoK v. 2.1, released 31 October 2019'''</center>") |
|||
| (13 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | There are many different types of | + | ---- |
| + | '''''Lead Author:''''' ''Sanford Friedenthal'', '''''Contributing Authors:''''' ''Dov Dori, Yaniv Mordecai'' | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | There are many different types of {{Term|Model (glossary)|models (glossary)}} expressed in a diverse array of modeling languages and tool sets. This article offers a taxonomy of model types and highlights how different models must work together to support broader {{Term|Engineering (glossary)|engineering}} efforts. | ||
==Model Classification== | ==Model Classification== | ||
| − | There are many different types of models and associated | + | There are many different types of models and associated {{Term|Modeling Language (glossary)|modeling languages}} to address different aspects of a system and different [[Types of Systems| types of systems]]. Since different models serve different {{Term|Purpose (glossary)|purposes}}, a classification of models can be useful for selecting the right type of model for the intended purpose and {{Term|Scope (glossary)|scope}}. |
===Formal versus Informal Models=== | ===Formal versus Informal Models=== | ||
| − | Since a | + | Since a {{Term|System (glossary)|system}} model is a representation of a system, many different expressions that vary in degrees of formalism could be considered models. In particular, one could draw a picture of a system and consider it a model. Similarly, one could write a description of a system in text, and refer to that as a model. Both examples are representations of a system. However, unless there is some {{Term|Agreement (glossary)|agreement}} on the meaning of the terms, there is a potential lack of precision and the possibility of ambiguity in the representation. |
| − | The primary focus of system modeling is to use models supported by a well-defined modeling language. While less formal representations can be useful, a model must meet certain expectations for it to be considered within the scope of | + | The primary focus of system modeling is to use models supported by a well-defined modeling language. While less formal representations can be useful, a model must meet certain expectations for it to be considered within the scope of {{Term|Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) (glossary)|model-based systems engineering (MBSE)}}. In particular, the initial classification distinguishes between informal and formal models as supported by a modeling language with a defined syntax and the {{Term|Semantics (glossary)|semantics}} for the relevant {{Term|Domain (glossary)|domain}} of interest. |
===Physical Models versus Abstract Models=== | ===Physical Models versus Abstract Models=== | ||
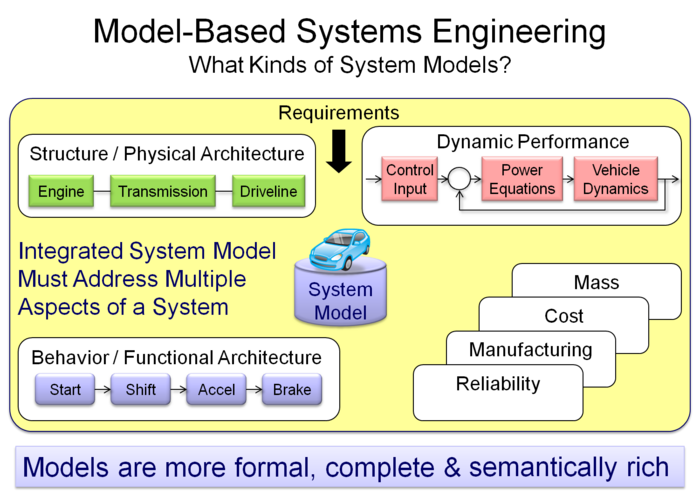
| − | The United States “Department of Defense Modeling and Simulation (M&S) Glossary” asserts that “a model can be [a] physical, mathematical, or otherwise logical representation of a system” (1998). This definition provides a starting point for a high level model classification. A | + | The United States “Department of Defense Modeling and Simulation (M&S) Glossary” asserts that “a model can be [a] physical, mathematical, or otherwise logical representation of a system” (1998). This definition provides a starting point for a high level model classification. A {{Term|Physical Model (glossary)|physical model}} is a concrete representation that is distinguished from the mathematical and logical models, both of which are more abstract representations of the system. The {{Term|Abstract Model (glossary)|abstract model}} can be further classified as descriptive (similar to logical) or analytical (similar to mathematical). Some example models are shown in Figure 1. |
[[File:Picture1.png|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 1. Model-Based Systems Engineering (Paredis 2011).''' Reprinted with permission of Chris Paredis from Georgia Tech. All other rights are reserved by the copyright owner.]] | [[File:Picture1.png|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 1. Model-Based Systems Engineering (Paredis 2011).''' Reprinted with permission of Chris Paredis from Georgia Tech. All other rights are reserved by the copyright owner.]] | ||
===Descriptive Models=== | ===Descriptive Models=== | ||
| − | A | + | A {{Term|Descriptive Model (glossary)|descriptive model}} describes logical relationships, such as the system's whole-part relationship that defines its parts tree, the interconnection between its parts, the {{Term|Function (glossary)|functions}} that its {{Term|Component (glossary)|components}} perform, or the test cases that are used to {{Term|Verification (glossary)|verify}} the system {{Term|Requirement (glossary)|requirements}}. Typical descriptive models may include those that describe the functional or physical {{Term|Architecture (glossary)|architecture}} of a system, or the three dimensional geometric representation of a system. |
===Analytical Models=== | ===Analytical Models=== | ||
| − | An | + | An {{Term|Analytical Model (glossary)|analytical model (glossary)}} describes mathematical relationships, such as differential equations that support quantifiable analysis about the system parameters. Analytical models can be further classified into dynamic and static models. Dynamic models describe the time-varying state of a system, whereas static models perform computations that do not represent the time-varying state of a system. A dynamic model may represent the performance of a system, such as the aircraft position, velocity, acceleration, and fuel consumption over time. A static model may represent the mass properties estimate or {{Term|Reliability (glossary)|reliability}} prediction of a system or component. |
===Hybrid Descriptive and Analytical Models=== | ===Hybrid Descriptive and Analytical Models=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 30: | ||
*properties of the system, such as performance, reliability, mass properties, power, structural, or thermal models; | *properties of the system, such as performance, reliability, mass properties, power, structural, or thermal models; | ||
| − | * | + | *{{Term|Design (glossary)|design}} and technology implementations, such as electrical, mechanical, and {{Term|Software (glossary)|software}} design models; |
| − | *subsystems and | + | *subsystems and {{Term|Product (glossary)|products}}, such as communications, fault management, or power distribution models; and |
*system applications, such as information systems, automotive systems, aerospace systems, or medical device models. | *system applications, such as information systems, automotive systems, aerospace systems, or medical device models. | ||
| − | The model classification, terminology and approach is often adapted to a particular application domain. For example, when modeling | + | The model classification, terminology and approach is often adapted to a particular application domain. For example, when modeling {{Term|Organization (glossary)|organization}} or {{Term|Business (glossary)|business}}, the {{Term|Behavior (glossary)|behavioral}} model may be referred to as workflow or {{Term|Process (glossary)|process}} model, and the performance modeling may refer to the {{Term|Cost (glossary)|cost}} and schedule performance associated with the organization or business process. |
A single model may include multiple domain categories from the above list. For example, a reliability, thermal, and/or power model may be defined for an electrical design of a communications subsystem for an aerospace system, such as an aircraft or satellite. | A single model may include multiple domain categories from the above list. For example, a reliability, thermal, and/or power model may be defined for an electrical design of a communications subsystem for an aerospace system, such as an aircraft or satellite. | ||
===System Models=== | ===System Models=== | ||
| − | System models can be hybrid models that are both descriptive and analytical. They often span several modeling domains that must be | + | System models can be hybrid models that are both descriptive and analytical. They often span several modeling domains that must be {{Term|Integration (glossary)|integrated}} to ensure a consistent and {{Term|Cohesion (glossary)|cohesive}} system representation. As such, the system model must provide both general-purpose system constructs and domain-specific constructs that are shared across modeling domains. A system model may comprise multiple views to support planning, requirements, design, analysis, and {{Term|Verification (glossary)|verification}}. |
| − | Wayne Wymore is credited with one of the early efforts to formally define a system model using a mathematical framework in ''A Mathematical Theory of Systems Engineering: The Elements'' (1967). Wymore established a rigorous mathematical framework for designing systems in a model-based context. A summary of his work can be found in [[A Survey of Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) Methodologies]]. | + | Wayne Wymore is credited with one of the early efforts to formally define a system model using a mathematical framework in ''A Mathematical Theory of Systems Engineering: The Elements'' (Wymore 1967). Wymore established a rigorous mathematical framework for designing systems in a model-based context. A summary of his work can be found in [[A Survey of Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) Methodologies]]. |
===Simulation versus Model=== | ===Simulation versus Model=== | ||
| − | The term | + | The term {{Term|Simulation (glossary)|simulation}}, or more specifically {{Term|Computer Simulation (glossary)|computer simulation}}, refers to a method for implementing a model over time (DoD 1998). The computer simulation includes the analytical model which is represented in executable code, the {{Term|Input (glossary)|input}} conditions and other input data, and the computing infrastructure. The computing infrastructure includes the computational engine needed to execute the model, as well as input and {{Term|Output (glossary)|output}} devices. The great variety of approaches to computer simulation is apparent from the choices that the designer of computer simulation must make, which include |
*stochastic or deterministic; | *stochastic or deterministic; | ||
| Line 48: | Line 51: | ||
*local or distributed. | *local or distributed. | ||
| − | Other classifications of a simulation may depend on the type of model that is being simulated. One example is an agent-based simulation that simulates the interaction among autonomous agents to predict | + | Other classifications of a simulation may depend on the type of model that is being simulated. One example is an agent-based simulation that simulates the interaction among autonomous agents to predict {{Term|Complex (glossary)|complex}} {{Term|Emergence (glossary)|emergent}} behavior (Barry 2009). They are many other types of models that could be used to further classify simulations. In general, simulations provide a means for analyzing complex dynamic behavior of systems, software, hardware, people, and physical phenomena. |
| − | Simulations are often integrated with the actual hardware, software, and operators of the system to evaluate how actual components and users of the system perform in a simulated | + | Simulations are often integrated with the actual hardware, software, and operators of the system to evaluate how actual components and users of the system perform in a simulated {{Term|Environment (glossary)|environment}}. Within the United States defense community, it is common to refer to simulations as live, virtual, or constructive, where live simulation refers to live operators operating real systems, virtual simulation refers to live operators operating simulated systems, and constructive simulations refers to simulated operators operating with simulated systems. The virtual and constructive simulations may also include actual system hardware and software in the loop as well as stimulus from a real systems environment. |
In addition to representing the system and its environment, the simulation must provide efficient computational methods for solving the equations. Simulations may be required to operate in real time, particularly if there is an operator in the loop. Other simulations may be required to operate much faster than real time and perform thousands of simulation runs to provide statistically valid simulation results. Several computational and other simulation methods are described in [[Simulation Modeling and Analysis]] (Law 2007). | In addition to representing the system and its environment, the simulation must provide efficient computational methods for solving the equations. Simulations may be required to operate in real time, particularly if there is an operator in the loop. Other simulations may be required to operate much faster than real time and perform thousands of simulation runs to provide statistically valid simulation results. Several computational and other simulation methods are described in [[Simulation Modeling and Analysis]] (Law 2007). | ||
| Line 58: | Line 61: | ||
==Integration of Models== | ==Integration of Models== | ||
| − | Many different types of models may be developed as artifacts of a MBSE effort. Many other domain-specific models are created for component design and analysis. The different descriptive and analytical models must be integrated in order to fully realize the benefits of a model-based approach. The role of MBSE as the models integrate across multiple domains is a primary theme in the International Council on Systems | + | Many different types of models may be developed as artifacts of a MBSE effort. Many other domain-specific models are created for component design and analysis. The different descriptive and analytical models must be integrated in order to fully realize the benefits of a model-based approach. The role of MBSE as the models integrate across multiple domains is a primary theme in the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) [[INCOSE Systems Engineering Vision 2020]] (INCOSE 2007). |
| − | As an example, system models can be used to specify the components of the system. The descriptive model of the system architecture may be used to identify and partition the components of the system and define their interconnection or other relationships. Analytical models for performance, physical, and other quality characteristics, such as reliability, may be employed to determine the required values for specific component properties to satisfy the system requirements. An | + | As an example, system models can be used to specify the components of the system. The descriptive model of the system architecture may be used to identify and partition the components of the system and define their interconnection or other relationships. Analytical models for performance, physical, and other quality characteristics, such as reliability, may be employed to determine the required values for specific component properties to satisfy the system requirements. An {{Term|Executable System Model (glossary)|executable system model}} that represents the interaction of the system components may be used to validate that the component requirements can satisfy the system behavioral requirements. The descriptive, analytical, and executable system model each represent different facets of the same system. |
| − | The component designs must satisfy the component requirements that are specified by the system models. As a result, the component design and analysis models must have some level of | + | The component designs must satisfy the component requirements that are specified by the system models. As a result, the component design and analysis models must have some level of {{Term|Integration (glossary)|integration}} to ensure that the design model is traceable to the requirements model. The different design disciplines for electrical, mechanical, and software each create their own models representing different facets of the same system. It is evident that the different models must be sufficiently integrated to ensure a cohesive system solution. |
| − | To support the integration, the models must establish | + | To support the integration, the models must establish {{Term|Semantic Interoperability (glossary)|semantic interoperability}} to ensure that a construct in one model has the same meaning as a corresponding construct in another model. This information must also be exchanged between modeling tools. |
| − | One approach to semantic interoperability is to use | + | One approach to semantic interoperability is to use {{Term|Model Transformation (glossary)|model transformations}} between different models. Transformations are defined which establish correspondence between the concepts in one model and the concepts in another. In addition to establishing correspondence, the tools must have a means to exchange the model data and share the transformation information. There are multiple means for exchanging data between tools, including file exchange, use of application program interfaces (API), and a shared repository. |
The use of [[Modeling Standards | modeling standards]] for modeling languages, model transformations, and data exchange is an important enabler of integration across modeling domains. | The use of [[Modeling Standards | modeling standards]] for modeling languages, model transformations, and data exchange is an important enabler of integration across modeling domains. | ||
| Line 72: | Line 75: | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
===Works Cited=== | ===Works Cited=== | ||
| + | Barry, P.S., M.T.K. Koehler, and B.F. Tivnan. 2009. ''Agent-Directed Simulation for Systems Engineering.'' McLean, VA: MITRE, March 2009, PR# 09-0267. | ||
| − | DoD. 1998. "'DoD Modeling and Simulation (M&S) Glossary" in ''DoD Manual 5000.59-M''. | + | DoD. 1998. "'DoD Modeling and Simulation (M&S) Glossary" in ''DoD Manual 5000.59-M''. Arlington, VA, USA: US Department of Defense. January 1998. |
| − | |||
| − | |||
Wymore, A. 1967. ''A Mathematical Theory of Systems Engineering: The Elements''. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley. | Wymore, A. 1967. ''A Mathematical Theory of Systems Engineering: The Elements''. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley. | ||
| Line 87: | Line 89: | ||
===Additional References=== | ===Additional References=== | ||
| − | + | Estefan, J. 2008. ''Survey of Candidate Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) Methodologies,'' Revision B. Pasadena, CA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), INCOSE-TD-2007-003-02. | |
| − | |||
| − | Estefan, J. 2008. ''Survey of Candidate Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) Methodologies,'' Revision B. Pasadena, CA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), INCOSE-TD-2007-003-02 | ||
| − | Hybertson, D. 2009. Model-Oriented Systems Engineering Science: A Unifying Framework for Traditional and Complex Systems. Boca Raton, FL, USA: Auerbach/CRC Press. | + | Hybertson, D. 2009.'' Model-Oriented Systems Engineering Science: A Unifying Framework for Traditional and Complex Systems''. Boca Raton, FL, USA: Auerbach/CRC Press. |
| − | INCOSE. 2007. ''[[INCOSE Systems Engineering Vision 2020|Systems Engineering Vision 2020]].'' Seattle, WA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering. September 2007. | + | INCOSE. 2007. ''[[INCOSE Systems Engineering Vision 2020|Systems Engineering Vision 2020]].'' Seattle, WA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering. September 2007. INCOSE-TP-2004-004-02. |
| − | Rouquette, N. and S. Jenkins. 2010. ''OWL Ontologies and SysML Profiles: Knowledge Representation and Modeling.'' Proceedings of the NASA-ESA PDE Workshop, June 2010 | + | Rouquette, N. and S. Jenkins. 2010. ''OWL Ontologies and SysML Profiles: Knowledge Representation and Modeling.'' Proceedings of the NASA-ESA PDE Workshop, June 2010. |
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 101: | Line 101: | ||
<center>[[Why Model?|< Previous Article]] | [[Representing Systems with Models|Parent Article]] | [[System Modeling Concepts|Next Article >]]</center> | <center>[[Why Model?|< Previous Article]] | [[Representing Systems with Models|Parent Article]] | [[System Modeling Concepts|Next Article >]]</center> | ||
| − | + | <center>'''SEBoK v. 2.1, released 31 October 2019'''</center> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Part 2]][[Category:Topic]] | [[Category:Part 2]][[Category:Topic]] | ||
[[Category:Representing Systems with Models]] | [[Category:Representing Systems with Models]] | ||
Revision as of 08:39, 28 October 2019
Lead Author: Sanford Friedenthal, Contributing Authors: Dov Dori, Yaniv Mordecai
There are many different types of models (glossary) expressed in a diverse array of modeling languages and tool sets. This article offers a taxonomy of model types and highlights how different models must work together to support broader engineering efforts.
Model Classification
There are many different types of models and associated modeling languages to address different aspects of a system and different types of systems. Since different models serve different purposes, a classification of models can be useful for selecting the right type of model for the intended purpose and scope.
Formal versus Informal Models
Since a system model is a representation of a system, many different expressions that vary in degrees of formalism could be considered models. In particular, one could draw a picture of a system and consider it a model. Similarly, one could write a description of a system in text, and refer to that as a model. Both examples are representations of a system. However, unless there is some agreement on the meaning of the terms, there is a potential lack of precision and the possibility of ambiguity in the representation.
The primary focus of system modeling is to use models supported by a well-defined modeling language. While less formal representations can be useful, a model must meet certain expectations for it to be considered within the scope of model-based systems engineering (MBSE). In particular, the initial classification distinguishes between informal and formal models as supported by a modeling language with a defined syntax and the semantics for the relevant domain of interest.
Physical Models versus Abstract Models
The United States “Department of Defense Modeling and Simulation (M&S) Glossary” asserts that “a model can be [a] physical, mathematical, or otherwise logical representation of a system” (1998). This definition provides a starting point for a high level model classification. A physical model is a concrete representation that is distinguished from the mathematical and logical models, both of which are more abstract representations of the system. The abstract model can be further classified as descriptive (similar to logical) or analytical (similar to mathematical). Some example models are shown in Figure 1.
Descriptive Models
A descriptive model describes logical relationships, such as the system's whole-part relationship that defines its parts tree, the interconnection between its parts, the functions that its components perform, or the test cases that are used to verify the system requirements. Typical descriptive models may include those that describe the functional or physical architecture of a system, or the three dimensional geometric representation of a system.
Analytical Models
An analytical model (glossary) describes mathematical relationships, such as differential equations that support quantifiable analysis about the system parameters. Analytical models can be further classified into dynamic and static models. Dynamic models describe the time-varying state of a system, whereas static models perform computations that do not represent the time-varying state of a system. A dynamic model may represent the performance of a system, such as the aircraft position, velocity, acceleration, and fuel consumption over time. A static model may represent the mass properties estimate or reliability prediction of a system or component.
Hybrid Descriptive and Analytical Models
A particular model may include descriptive and analytical aspects as described above, but models may favor one aspect or the other. The logical relationships of a descriptive model can also be analyzed, and inferences can be made to reason about the system. Nevertheless, logical analysis provides different insights than a quantitative analysis of system parameters.
Domain-specific Models
Both descriptive and analytical models can be further classified according to the domain that they represent. The following classifications are partially derived from the presentation on OWL, Ontologies and SysML Profiles: Knowledge Representation and Modeling (Web Ontology Language (OWL) & Systems Modeling Language (SysML)) (Jenkins 2010):
- properties of the system, such as performance, reliability, mass properties, power, structural, or thermal models;
- design and technology implementations, such as electrical, mechanical, and software design models;
- subsystems and products, such as communications, fault management, or power distribution models; and
- system applications, such as information systems, automotive systems, aerospace systems, or medical device models.
The model classification, terminology and approach is often adapted to a particular application domain. For example, when modeling organization or business, the behavioral model may be referred to as workflow or process model, and the performance modeling may refer to the cost and schedule performance associated with the organization or business process.
A single model may include multiple domain categories from the above list. For example, a reliability, thermal, and/or power model may be defined for an electrical design of a communications subsystem for an aerospace system, such as an aircraft or satellite.
System Models
System models can be hybrid models that are both descriptive and analytical. They often span several modeling domains that must be integrated to ensure a consistent and cohesive system representation. As such, the system model must provide both general-purpose system constructs and domain-specific constructs that are shared across modeling domains. A system model may comprise multiple views to support planning, requirements, design, analysis, and verification.
Wayne Wymore is credited with one of the early efforts to formally define a system model using a mathematical framework in A Mathematical Theory of Systems Engineering: The Elements (Wymore 1967). Wymore established a rigorous mathematical framework for designing systems in a model-based context. A summary of his work can be found in A Survey of Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) Methodologies.
Simulation versus Model
The term simulation, or more specifically computer simulation, refers to a method for implementing a model over time (DoD 1998). The computer simulation includes the analytical model which is represented in executable code, the input conditions and other input data, and the computing infrastructure. The computing infrastructure includes the computational engine needed to execute the model, as well as input and output devices. The great variety of approaches to computer simulation is apparent from the choices that the designer of computer simulation must make, which include
- stochastic or deterministic;
- steady-state or dynamic;
- continuous or discrete; and
- local or distributed.
Other classifications of a simulation may depend on the type of model that is being simulated. One example is an agent-based simulation that simulates the interaction among autonomous agents to predict complex emergent behavior (Barry 2009). They are many other types of models that could be used to further classify simulations. In general, simulations provide a means for analyzing complex dynamic behavior of systems, software, hardware, people, and physical phenomena.
Simulations are often integrated with the actual hardware, software, and operators of the system to evaluate how actual components and users of the system perform in a simulated environment. Within the United States defense community, it is common to refer to simulations as live, virtual, or constructive, where live simulation refers to live operators operating real systems, virtual simulation refers to live operators operating simulated systems, and constructive simulations refers to simulated operators operating with simulated systems. The virtual and constructive simulations may also include actual system hardware and software in the loop as well as stimulus from a real systems environment.
In addition to representing the system and its environment, the simulation must provide efficient computational methods for solving the equations. Simulations may be required to operate in real time, particularly if there is an operator in the loop. Other simulations may be required to operate much faster than real time and perform thousands of simulation runs to provide statistically valid simulation results. Several computational and other simulation methods are described in Simulation Modeling and Analysis (Law 2007).
Visualization
Computer simulation results and other analytical results often need to be processed so they can be presented to the users in a meaningful way. Visualization techniques and tools are used to display the results in various visual forms, such as a simple plot of the state of the system versus time to display a parametric relationship. Another example of this occurs when the input and output values from several simulation executions are displayed on a response surface showing the sensitivity of the output to the input. Additional statistical analysis of the results may be performed to provide probability distributions for selected parameter values. Animation is often used to provide a virtual representation of the system and its dynamic behavior. For example, animation can display an aircraft’s three-dimensional position and orientation as a function of time, as well as project the aircraft’s path on the surface of the Earth as represented by detailed terrain maps.
Integration of Models
Many different types of models may be developed as artifacts of a MBSE effort. Many other domain-specific models are created for component design and analysis. The different descriptive and analytical models must be integrated in order to fully realize the benefits of a model-based approach. The role of MBSE as the models integrate across multiple domains is a primary theme in the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) INCOSE Systems Engineering Vision 2020 (INCOSE 2007).
As an example, system models can be used to specify the components of the system. The descriptive model of the system architecture may be used to identify and partition the components of the system and define their interconnection or other relationships. Analytical models for performance, physical, and other quality characteristics, such as reliability, may be employed to determine the required values for specific component properties to satisfy the system requirements. An executable system model that represents the interaction of the system components may be used to validate that the component requirements can satisfy the system behavioral requirements. The descriptive, analytical, and executable system model each represent different facets of the same system.
The component designs must satisfy the component requirements that are specified by the system models. As a result, the component design and analysis models must have some level of integration to ensure that the design model is traceable to the requirements model. The different design disciplines for electrical, mechanical, and software each create their own models representing different facets of the same system. It is evident that the different models must be sufficiently integrated to ensure a cohesive system solution.
To support the integration, the models must establish semantic interoperability to ensure that a construct in one model has the same meaning as a corresponding construct in another model. This information must also be exchanged between modeling tools.
One approach to semantic interoperability is to use model transformations between different models. Transformations are defined which establish correspondence between the concepts in one model and the concepts in another. In addition to establishing correspondence, the tools must have a means to exchange the model data and share the transformation information. There are multiple means for exchanging data between tools, including file exchange, use of application program interfaces (API), and a shared repository.
The use of modeling standards for modeling languages, model transformations, and data exchange is an important enabler of integration across modeling domains.
References
Works Cited
Barry, P.S., M.T.K. Koehler, and B.F. Tivnan. 2009. Agent-Directed Simulation for Systems Engineering. McLean, VA: MITRE, March 2009, PR# 09-0267.
DoD. 1998. "'DoD Modeling and Simulation (M&S) Glossary" in DoD Manual 5000.59-M. Arlington, VA, USA: US Department of Defense. January 1998.
Wymore, A. 1967. A Mathematical Theory of Systems Engineering: The Elements. New York, NY, USA: John Wiley.
Wymore, A. 1993. Model-Based Systems Engineering. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Primary References
Law, A. 2007. Simulation Modeling and Analysis, 4th ed. New York, NY, USA: McGraw Hill.
Wymore, A. 1993. Model-Based Systems Engineering. Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press.
Additional References
Estefan, J. 2008. Survey of Candidate Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) Methodologies, Revision B. Pasadena, CA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), INCOSE-TD-2007-003-02.
Hybertson, D. 2009. Model-Oriented Systems Engineering Science: A Unifying Framework for Traditional and Complex Systems. Boca Raton, FL, USA: Auerbach/CRC Press.
INCOSE. 2007. Systems Engineering Vision 2020. Seattle, WA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering. September 2007. INCOSE-TP-2004-004-02.
Rouquette, N. and S. Jenkins. 2010. OWL Ontologies and SysML Profiles: Knowledge Representation and Modeling. Proceedings of the NASA-ESA PDE Workshop, June 2010.