Difference between revisions of "Service Systems Background"
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
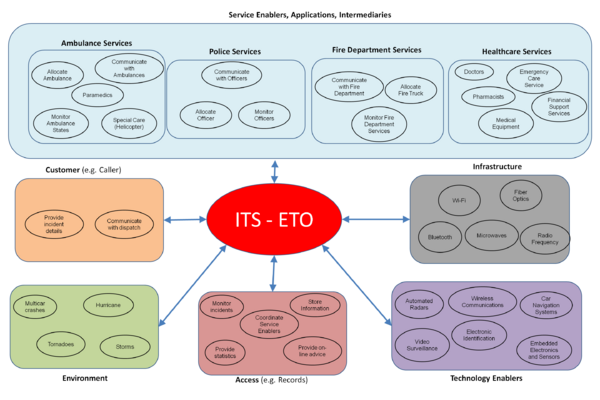
The Service System Context Diagram shown below lists the possible stakeholders in a Service System. | The Service System Context Diagram shown below lists the possible stakeholders in a Service System. | ||
| − | [[File:SSE_SSB_Fig1.png| | + | [[File:SSE_SSB_Fig1.png|600px|Service System Context Diagram]] |
Figure 1. Service System Context Diagram | Figure 1. Service System Context Diagram | ||
Revision as of 01:53, 5 August 2011
Evolution Toward Service-Based Economies
Economies are pre-disposed to follow a developmental progression that moves them from heavy reliance on agriculture and mining, toward the development of manufacturing and finally toward more service-based economic activity. As reported by the Organization for Economic Co-Operation and Development (OECD), in its “Science, Technology Industry (STI) Forum” The Service Economy:
“The reason that we see a services economy today, and gather to talk about it and recognize its importance is because technology has allowed service industries to gain the operational leverage that manufacturing achieved 100 years ago. In addition to banks, health systems, telephone and telecommunications networks, and distribution and retailing firms are further examples of sectors that have been able to benefit from economies of scale. As a result, we are now living in a world where global-scale service companies exist for the first time, whereas we have seen global manufacturing companies for 50 years or more” [OECD 2000].
The typical industry example given of this progression toward service is IBM. Even though it still produces hardware, they view their business as overwhelmingly service-oriented where hardware plays only an incidental role in their business solutions services; the fastest line of business growth within IBM has been the Business-to-Business (B2B) Services: IT (data center, call centers), Business Process Outsourcing/Reengineering, Systems Integration, and organizational change.
Business to Government (B2G) is forecasted to have the fastest growth in the years to come [Spohrer 2011]. For IBM, this trend started in 1989 with the launch of Business Recovery Services; it accelerated with the acquisition of Price-Waterhouse Coopers Consultants in 2002 and culminated with the sale of the laptop (ThinkPad) manufacturing, their last major hardware operation during 2005.
IBM exemplifies a trend which has accelerated in the last 25-30 years so that in 2006, services produced by private industry accounted for 67.8 percent of U.S. gross domestic product. The top subsectors included real estate and financial, healthcare, education, legal, banking, insurance, and investment. Production of goods was 19.8 percent of GDP. The top product subsectors include manufacturing, construction, oil and gas, mining, and agriculture [Moran 2006].
Product Service Systems (PSS)
Beginning in the mid 1990’s, the concept of a product-service system (PSS) started to evolve. PSS’s have been adopted by businesses interested in using the model to bring not only added value to their existing offerings, but capital-intensive, environmentally favorable products to market [Mont and Tukker 2006].
There are some definitional issues in any discussion of PSS including the fact that services are products, and services invariably need physical products to support their provision or delivery [Mont and Tukker, 2006]. A PSS is comprised of tangibles and intangibles (activities) in combination to fulfill specific customer requirements, or ideally, to allow applications to be co-created flexibly by linking loosely-coupled agents, typically over a network [Domingue, 2009]. Research has shown that manufacturing firms are more amenable to producing "results", rather than solely products as specific artifacts and that end-user are more amenable to consuming such results. [Cook 2004]; [Wild et al. 2007].
The popularity of Wikis, Blogs, and Social Networking tools is strong evidence that Enterprise 2.0 is already well under way; Andrew McAfee describes Enterprise 2.0 as "the use of emergent social software platforms within companies, or between companies and their partners or customers". However, the integrated access to people, media, services, and things, provided by the future Internet, will enable new styles of societal and economic interactions at unprecedented scale, flexibility, and quality. These applications will exploit the wisdom of crowds and allow for mass collaboration and value co-creation. [McAfee 2009].
The Future Internet will provide location independent, interoperable, scalable, secure, and efficient access to a coordinated set of services [Tselentis et al. 2009] but such broad vision demands a sound and well-defined approach for management and governance.
Service Based Applications
Current application service providers like Amazon, Facebook, Tweeter, eBay, and Google must mediate between the business challenges enabled by network and IT convergence and customers (enterprise or consumer) demanding new and more value-adding services enabled by social networks [TMFORUM 2008]. The differences between IT and Communications technologies are disappearing; the enterprise internally focused processes (back-stage processes) for operations optimization are now being strongly tied to the customer facing (front-stage) processes for value co-creation and delivery.
In this scenario the enterprise’s internal organization and employees are embedded in the service value chain to benefit customers and stakeholders. In the service-dominant logic (S-DL) for marketing [Vargo and Lusch 2004] service is the application (through deeds, processes, and performances) of specialized operant resources (knowledge and skills) for the benefit of another entity or the entity itself. The emphasis is thus on the process of doing something for and with another entity in order to create value; for Service Science [Maglio et al. 2006; Maglio and Spohrer 2008] service is a system of interacting and interdependent parts (people, technologies and organizations) that is externally oriented to achieve and maintain a sustainable competitive advantage.
The future Internet is expected to be more agile, scalable, secure, and reliable; such rapidly emerging applications with different requirements and implications for the future Internet design pose a significant set of problems and challenges; in particular “the fragmentation of knowledge and the isolation of specialist as well as the need to find new approaches to problems created by earlier ‘solution of problems’” [Skyttner 2006]. Service Systems Engineering disciplines may inform the discussion and offer potential multidisciplinary environments and trans-disciplinary solutions.
The Internet has been successfully deployed for several decades due to its high flexibility in running over different physical media and supporting different high-layer protocols and applications, including traditional file transfer, email, and client-server-based web applications, among others.
Business Dependence on Service Systems
Most people and enterprises are heavily dependent on service interactions including entertainment, communications, retail, education, healthcare, etc. brought about by emerging services (video on demand, web conferencing, time-shift services, place-shift and device-shift services, Enterprise Applications (e.g., ERP, CRM, MRM, SCM, etc.), Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Cloud Services, Managed Peer-to-Peer Services, etc.); a common denominator of the set of services mentioned is that applications are offered as services by the interaction of Service Systems entities and thus they are Service Based Applications (SBA).
Thus, “A Service Based Application is obtained by composing various Service System entities to satisfy the desired functionality” [Andrikopoulos, et al., 2010]. SBAs are heavily dependent on web services development (Web Services 2.0 or WS-) and thus Software Systems Engineering (SwSE) plays a very important role. However, another critical role is played by Human Interfaces and Technology Development; for instance governance (rules & regulations) and technology research and development is required for future services like healthcare services, intelligent transportation services, environmental services, etc. to address societal challenges of the 21st century (sustainability, energy, etc.) as presented by [Vest 2010] if we were to face those challenges as an eco-system.
ITS Service System Example
Let’s analyze an Intelligent Transport System-Emergency Transportation Operations (ITS-ETO). In an ITS-ETO the service goal is to provide safe evacuation, prompt medical care, and improved emergency management service. Typically, a traveler can request service through an emergency call or automated crash report feature or a public safety officer on location can request the service customer feature and access rights.
The ITS-ETO Service System utilizes advances in communication and information systems to access essential real-time data about conditions on routes throughout the affected area (technology and information enabler) and coordinates operational and logistical strategies in cooperation within all service entities (organization processes). In a critical emergency situation, when patient conditions are continuously changing ITS can help identify the appropriate response and get the correct equipment (infrastructure enabler) such as a helicopter and emergency personnel (people enabler) to and from the scene quickly and safely.
Efficient and reliable voice, data, and video communications (application enabler) further provide agencies with the ability to share information related to the status of the emergency, the operational conditions of the transportation facilities, and the location of emergency response resources to help communicate and coordinate operations and resources in real time. Advances in logistical and decision-making tools can enable commanders and dispatchers to implement strategies as conditions change (decision making).
It is also critical to receive information on the environmental conditions (storm, hurricanes, hazardous materials, complex multi-vehicle crashes etc.) and/or closures when coordinating evacuations. The availability of real-time data on transportation conditions, coupled with decision-making tools, enables more effective response and coordination of resources during emergencies. ITS-ETO also enhances the ability of transportation agencies to coordinate response with other stakeholders.
As a result, increased data accuracy, timeliness, and automation leads to use of fewer resources, reuse of exchanges, resulting in time and cost savings. Enhanced response and management leads to greater situational awareness and more effective response with the ability to identify and utilize the appropriate equipment resulting in a more efficient response at the right time (output). [US DOT 2011]
The Service System Context Diagram shown below lists the possible stakeholders in a Service System.
Figure 1. Service System Context Diagram
As seen in the above example the service activities are knowledge-intensive; well defined linkages (including access rights) and relationships among different entities give rise to the needed service systems interactions for the service system to be successful. As the world becomes more widely interconnected and people become better educated the services networks created by the interaction of the service systems will be accessible from anywhere, anytime by anyone with the proper access rights.
Knowledge agents are then humans creating new linkages of information to create new knowledge which “can later be embedded in other people, technology, shared information, and organizations”. Thus people can be considered individual service systems with: “finite lifecycles, identities (with associated histories and expectations), legal rights and authority to perform certain functions, perform multitasking as a way to increase individual productivity output in a finite time, and engage in division-of-labor with others to increase collective productive output in finite time” [Spohrer and Kwan 2009]
References
Citations
Cook, M. 2004. Understanding The Potential Opportunities Provided by Service-Orientated Concepts to Improve Resource Productivity. Design and Manufacture for Sustainable Development 2004. Eds. Bhamra, T. Hon, B. John Wiley and Sons: 125. ISBN: 978-1-86058-470-1.
Domingue, J., Fensel, D., Davies, J., González-Cabero, R., Pedrinaci, C. 2009. The Service Web: a Web of Billions of Services. Towards the Future Internet- A European Research Perspective. Eds. Tselentis et al. IOS Press. Doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-007-0-183.
Maglio P. and Spohrer, J. 2008. Fundamentals of Service Science. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science 36 (1): 18-20. DOI: 10.1007/s11747-007-0058-9.
Mont, O. and Tukker, A. 2006. Product-Service Systems. Journal of Cleaner Production 14: 1451-1454.
Moran, M. 2006. Servicizing Solar Panels. LUMES Department Industry Course Report. Lund University, Sweden.
McAfee, A. 2009. Enterprise 2.0: New Collaborative Tools for Your Organization's Toughest Challenges. Harvard Business School Press, ISBN-10: 1422125874; ISBN-13: 978-1422125878.
Skyttner, L. 2006. General Systems Theory: Perspectives, Problems, Practice. World Scientific Publishing Company. 2nd Edition. ISBN-10: 981256389; ISBN-13: 978-9812563897.
Spohrer, J.C. 2011. Service Science: Progress & Directions. International Joint Conference on Service Science. Taipei, Taiwan.
Spohrer, J. and Kwan, S.K. 2009. Service Science, Management, Engineering, and Design (SSMED): An Emerging Discipline-Outline & References. International Journal of Information Systems in the Service Sector 1(3).
TMFORUM. 2008. Service Delivery Framework Overview. (TR139 Version 2.0, July 2008).
Tselentis, G., Domingue, J., Galis, A., Gavras, A., Hausheer, D., Krco, S., Lotz, V., and Zahariadis, T. 2009. Towards the Future Internet - A European Research Perspective. IOS Press. Doi:10.3233/978-1-60750-007-0-183.
Vargo, S. L. and Lusch, R. F. 2004. The Four Service Marketing Myths – Remnants of a Goods-Based Manufacturing Model. Journal of Service Research 6: 324-335.
Wild, P.J., Jupp, J., Kerley, W., Eckert, C., and Clarkson, P.J. 2007. Towards A Framework for Profiling of Products and Services. 5th International Conference on Manufacturing Research (ICMR 2007).
Primary References
Maglio, P., Kieliszewski C., and Spohrer, J. 2010. Handbook of Service Science. Springer. 1st Edition. ISBN-10: 9781441916273; ISBN-13: 978-1441916273.
McAfee, A. 2009. Enterprise 2.0: New Collaborative Tools for Your Organization's Toughest Challenges. Harvard Business School Press, ISBN-10: 1422125874; ISBN-13: 978-1422125878.
Mont, O. and Tukker, A. 2006. Product-Service Systems. Journal of Cleaner Production 14: 1451-1454.
TMFORUM. 2008. Service Delivery Framework Overview. (TR139 Version 2.0, July 2008).
Additional References
All additional references should be listed in alphabetical order.