Difference between revisions of "Scope of Service Systems Engineering"
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
Hsu, C. 2009. "Service Science and Network Science." ''Service Science 1'' (2): i-ii. | Hsu, C. 2009. "Service Science and Network Science." ''Service Science 1'' (2): i-ii. | ||
| − | ITIL V3. 2007. ITIL Lifecycle Publication Suite Books. The Stationery Office. ISBN | + | ITIL V3. 2007. ''"ITIL Lifecycle Publication Suite Books."'' London, UK: The Stationery Office. ISBN 978-0-11331-050-0. |
Maglio, P., Weske, M., Yang, J., and Fantinato, M. (Eds.). 2010. ICSOC 2010. Springer-Verlag. ISBN-13: 978-3-642-17357-8. | Maglio, P., Weske, M., Yang, J., and Fantinato, M. (Eds.). 2010. ICSOC 2010. Springer-Verlag. ISBN-13: 978-3-642-17357-8. | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 2 September 2011
Enterprises plan, develop and manage the enhancements of their infrastructure, products, and services, including marketing strategies for product and service offerings. These plans propose new products or service offerings based on new, unexplored or unforeseen customer needs with clearly differentiated value propositions. Service strategies are the internal business processes required to design, operate and deliver services. The mission of Service Strategies is to develop the capacity to achieve and maintain a strategic advantage. (ITIL V3 2007)
Taking the Systems Engineering (SE) approach to Service Systems, or service systems engineering (SSE), is imperative for the service-oriented, customer-centric, holistic view to select and combine Service System entities. The SSE approach can then define, and discover relationships among Service System entities, to plan, design, adapt or self-adapt to co-create value. The SSE approach should identify linkages, relationships, constraints, challenges/problems, new technologies, interoperability standards, interface agreements or process development requirements among service entities required for the planned service or for potential future services. (Lefever 2005)
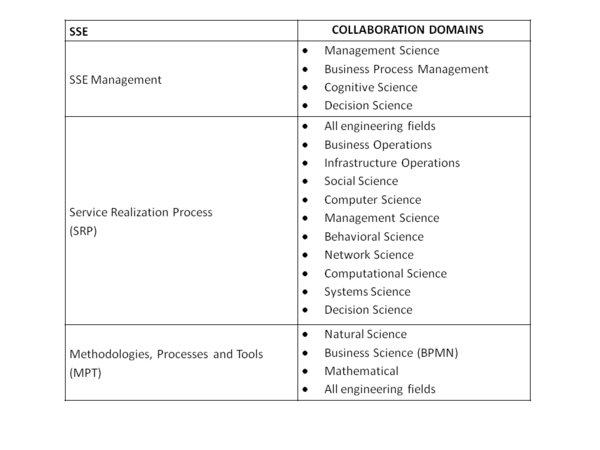
SSE mandates participation not only from engineering, business, operations and customers but also from different domains that range from Management Science, Behavioral Science, Social Science, Systems Science, Network Science, Computer Science, Decision Informatics, etc.
Hipel et. al. (2007) have presented a Table for service science in terms of the Domains & Methods including not only Service Systems but also Infrastructure & Transportation Systems, Environmental & Energy Systems and Defense & Space Systems. The collaboration domains in the Figure below are a first approximation to the collaboration required from different disciplines for the SSE paradigm.
Figure 1. SSE Domain Collaboration
Major challenges faced by SSE include the dynamic nature of Service Systems evolving and adapting to constantly changing operations and/or business environments and the need to overcome silos of knowledge. Interoperability of Service System entities through interface agreements must be at the forefront of the SSE design process for the harmonization of Operations, Administration, Maintenance and Provisioning procedures of the individual Service System entities. (Pineda 2010)
In addition, Service Systems require open collaboration among all stakeholders but recent research on mental models of multidisciplinary team’s integration and collaboration into cohesive teams have proven to be a major challenge. (Carpenter et al. 2010) (See also Team Dynamics) Thus, the emphasis on multidisciplinary (scientific, engineering, management, social) education and training programs required to foster systems thinking helps bridge the gaps created by these silos of knowledge.
In the SSE approach the social, governance, business, service, operations, and management activities are linked together through the Service life cycle ; Service Systems are by themselves a type of System of Systems (SoS) where traditional systems engineering (TSE) practices need to be extended to include services systems entities relationships (interface agreements among people, organizations, processes and technologies) through information flows, technical interoperability, governance and access rights within a system of systems.
Interoperability of Services
Interoperability among the different Service System entities becomes highly relevant in SSE since the constituent entities are designed according to stakeholder needs; the entity is usually managed and operated to satisfy its own objectives independently of other system entities. The objectives of individual Service System entities may not necessarily converge with the overall objectives of the service system. Thus, the need to include in the definition, analysis and design of the service system governance frameworks to align political objectives, service strategies, business objectives, information and communications technologies (ICT) objectives, technology objectives and end-to-end Operations Administration and Maintenance procedures and allocation of these procedures to individual entities. (Luzeaux and Ruault 2010)
For the sake of completeness of the description, in the previous discussion relates to a new Service System development. There may be instances where a service is planned for delivery in phases of deployment (Transition/Deployment phase) or as presented earlier, if there is already a Service System defined and deployed then it may be that the new request is a Service Based Applications (SBA) in which case the process is more of adaptations needed to existing Service System to deploy the new application. For SBA instances advances in Computer Engineering, Computer Science and Software development already permit the adaptation and creation of SBA in a run-time environment for the discovery, development and publishing of applications. (Maglio et al. 2010)
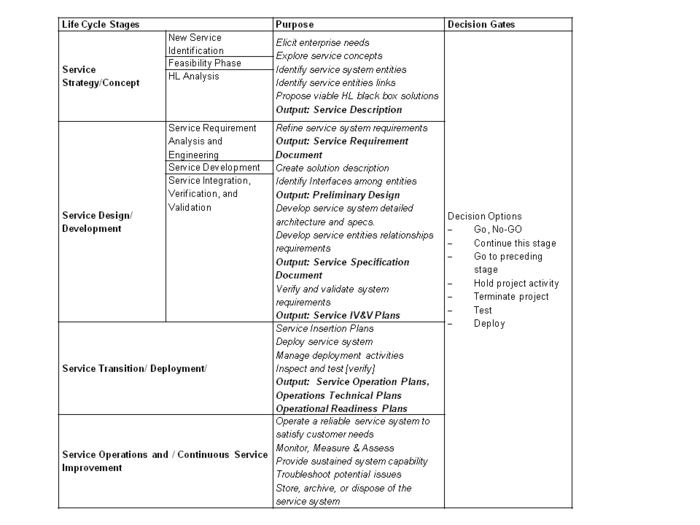
The Service Design Process (SDP) for new services is triggered by the market concept of the intended service including considerations such as the stakeholder(s), service value chain(s), target market(s), target customer(s), proposed SLA, demand forecast, pricing strategy, customer access privileges, which together comprise The Service strategy. The SDP process then adapts the TSE as a Life Cycle Approach (Concept/Definition, Design/Development, Deployment/Transition, Operations, Lifecycle Management/Utilization/CSI and Retirement) as discussed earlier and in the ISO/IEC 15288 Generic Life Cycle Stages (ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288). A more detailed list of the SSE Process activities is described in later sections.
Service Lifecycle Stages
The SDP stages and notation are depicted in the Figure below; due to the complexity of service systems the documents generated are becoming more Model Based electronic than written binders depending on methodologies and tools used.
Figure 2. Service Design Process: Life Cycle Stages.
We have included all the Life Cycle stages for completeness, but very often during the concept analysis phase it may be determined that not all stages are needed. In these cases, a recommendation should be made about which stages are specifically required for the realization of the service in question.
Service Design Management
Another important role of Service Systems Engineering is the Management of the Service Design Process. SSE utilizes TSE practices to manage the resource and asset allocation to perform the activities required to realize the service through the value chain both for the customer and the service provider. The main focus of the Service Design Process management is to provide for the planning, organizational structure, collaboration environment and program controls to ensure that stakeholders needs are met from an end-to-end customer perspective.
The Service Design Process management process aligns business objectives and business operational plans with end-to-end service objectives including customer management plans, service management and operations plans, operations technical plans, and technical plans. The main SSE Management activities are:
- SSE Planning
- SSE Assessment and Control
- SSE Decision Management
- SSE Risk Management
- SSE Configuration Management
- SSE Information Management
- SSE Engineering Measurement
SSE plays a critical role in describing the needs of the intended service in terms of the Service day-to-day operations including customer care center requirements, interface among Service System entities such as: Manufacturing Plant, Smart Grid, Hospital, network infrastructure provider(s), content provider(s) and service provider(s), service based application provider(s), applications providers and the Customer Management Process for the service.
Current Research in Computer Engineering and Software Systems Engineering is looking at the development of run-time platforms to allow real time or near real time customer service discovery and publishing (Spark 2009). The Service centric Systems Engineering (ScSE) consortium has a well defined Service Design process that is being applied to SBA. In this approach there are design time and run-time sub-processes for the composition, provisioning, orchestration and testing for service publishing (Lefever 2005). There is particular interest from the research community to include Human-Computer Interactions (HCI) and Behavioral Science to address Current Social Networking Services (Facebook, Twitter, Linkdln, Google+, etc.) used to share unverified information via audio, messaging, video, chats, etc.
This research is gaining relevance because of the thin line between the customer (consumer, enterprise) and content providers in regards to security, privacy, information authentication and possible misuse of the user generated content. Even as the research progresses, these networking services are examples of business models organizing communities of interest for innovation. “If we understand this networking, then we may be able to see through the business strategies and systems design laws that optimize connected value co-creation”. (Hsu 2009)
References
Citations
Carpenter, S., Delugach, H., Etzkorn, L., Fortune, J., Utley, D, and Virani, S. 2010. "The Effect of Shared Mental Models on Team Performance." Presented at Industrial Engineering Research Conference, Institute of Industrial Engineers. Cancun, Mexico.
Hipel, K.W., Jamshidi, M.M., Tien, J.M., and White, C.C. 2007. "The Future of Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Application Domains and research Methods." IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part C: Applications and Reviews 37 (5): 726-743.
Hsu, C. 2009. "Service Science and Network Science." Service Science 1 (2): i-ii.
ITIL V3. 2007. "ITIL Lifecycle Publication Suite Books." London, UK: The Stationery Office. ISBN 978-0-11331-050-0.
Maglio, P., Weske, M., Yang, J., and Fantinato, M. (Eds.). 2010. ICSOC 2010. Springer-Verlag. ISBN-13: 978-3-642-17357-8.
Pineda, R. 2010. Understanding Complex System of Systems Engineering. International Engineering Network Plenary. Metz, France.
Spark, D., 2009. Real-Time Search and Discovery of the Social Web. Spark Media Solutions Report. http://sparkmediasolutions.com/. accessed on June 3rd 2011.
Primary References
Chang. 2010. Service Systems Management and Engineering: Creating Strategic Differentiation and Operational Excellence, Chang C.M., John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2010, ISBN 978-0-470-42332-5.
ITIL V3. 2007. ITIL Lifecycle Publication Suite Books. The Stationery Office. ISBN: 978-0113310500.
Lefever, B. 2005. SeSCE Methodology Overview. Service Centric Systems Engineering. Luzeaux, D. and Ruault, J.R. 2010. System of Systems. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN # 978-1-84821-164-3.
Maglio, P., Weske, M., Yang, J., and Fantinato, M. (Eds.). 2010. Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Service Oriented Computing: ICSOC 2010. Springer-Verlag. ISBN-13: 978-3-642-17357-8.
Additional References
All additional references should be listed in alphabetical order.
Article Discussion
Signatures
--Blawson 20:40, 15 August 2011 (UTC)