Difference between revisions of "Enabling Businesses and Enterprises"
Wikiexpert (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 93: | Line 93: | ||
===Primary References=== | ===Primary References=== | ||
| − | + | Blockley,D. and Godfrey, P. 2000. ''[[Doing It Differently – Systems For Rethinking Construction]]''. London, UK: Thomas Telford, Ltd. | |
===Additional References=== | ===Additional References=== | ||
Revision as of 17:49, 20 June 2012
To enable systems engineering within a business or enterprise (hereafter just called "business" as a shorthand because a business is a specific type of enterprise that usually has sufficiently strong central authority and motivation to take steps to enable systems engineering (SE)), the business could establish a strong central governance approach to how SE is managed across its various components, projects, programs, and teams; e.g., the business could mandate a standard SE process, career path, technical authority, and toolset to be used by all systems engineers in the business. Clearly, the feasibility of that approach would depend on the authority of the business management. Some businesses have sufficiently centralized authority that such a mandate could be issued, supported, and enforced. For others with decentralized authority, this would not be possible or practical. At the other extreme, the business could allow each component and team to establish its own way in governing SE, making independent decisions about process, career path, technical authority, and toolsets. Most large businesses use a blend of approaches that fit the culture, context, purpose, and personalities of the business. A business is itself a system and can benefit from being viewed that way. The information on systems offered throughout the SEBoK can help enable a business to better perform SE.
To download a PDF of all of Part 5 (including this knowledge area), please click here.
Topics
This knowledge area contains the following topics:
- Deciding on Desired Systems Engineering Capabilities within Businesses and Enterprises
- Organizing Business and Enterprises to Perform Systems Engineering
- Assessing Systems Engineering Performance of Business and Enterprises
- Developing Systems Engineering Capabilities within Businesses and Enterprises
- Culture
Businesses usually adopt or enhance their SE capability for one of four reasons:
- To do current business better (typically a combination of faster, better, cheaper)
- To respond to a disruption in the market place requiring them to change the way they do business - a competitive threat or new demands from customers
- To reposition the business in its value chain or open up a new market
- To develop a new generation product or service.
Logical flow between topics
The way in which they enable SE should be driven by those reasons, tempered by the context, culture, and other factors in which the business operates.
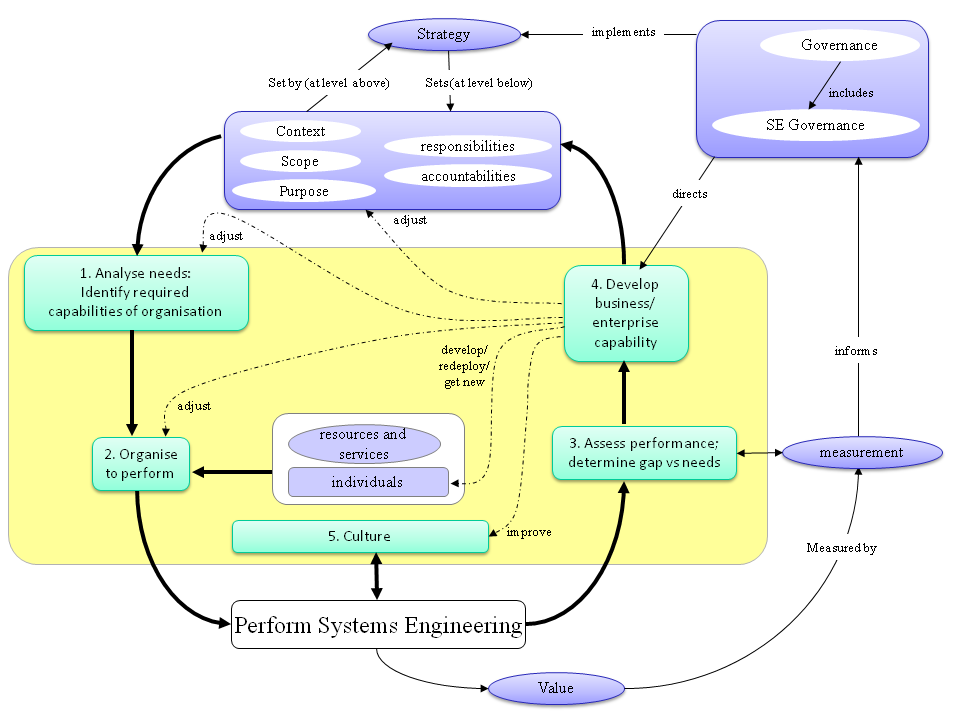
One illustrative flow between the topics is shown in the Figure 1 diagram, which is essentially a "plan-do-check-act" cycle (Deming 1994).
Analyze Needs
- Systems Engineering Governance sets the Systems Engineering Organizational Strategy, which is constrained by the purpose, context, scope, responsibilities and accountabilities of the business. These may be developed by Enterprise Systems Engineering or Capability Engineering activities, and/or flowed down from the level above, and/or negotiated with peers
- The business assesses what SE capabilities it needs to fulfill its Organizational Purpose; that assessment may include participation of stakeholders from across the business, such as the business executive team, and leaders from various groups such as engineering, finance, and marketing; (see Deciding on Desired Systems Engineering Capabilities within Businesses and Enterprises).
Organize to Perform
- The business organizes to perform SE, allocating responsibilities and resources to the various actors responsible for SE activities (see Organizing Business and Enterprises to Perform Systems Engineering)
Perform Systems Engineering
- SE is performed in support of business products and services (see Systems Engineering and Management in Part 3)
Assess Performance; Determine Gaps Versus Needs
- Performance is assessed (see Assessing Systems Engineering Performance of Business and Enterprises )
- Any gap between needed and achieved performance is identified.
Develop Business/Enterprise Capability
If there is a gap between actual and needed capabilities, measures are taken to develop or improve the capabilities using the available levers to:
- Develop, redeploy or obtain new facilities, tools, services, and individuals;
- Improve culture;
- Adjust organization;
- Adjust and align measures, goals and incentives;
- Adjust the definition of the required capabilities;
- If necessary, renegotiate scope, context, purpose, responsibility and accountability.
(See Developing Systems Engineering Capabilities within Businesses and Enterprises)
Businesses vary enormously in purpose, scope, size, culture and history. The way the business prepares to perform Systems Engineering needs to be tailored according to the specific situation and will depend greatly on the level of understanding of the added value of systems engineering, as well as the organization's maturity and homogeneity.
This Knowledge Area discusses the implementation of SE in business and in enterprise , and is also relevant to extended enterprises and to projects that involve multiple organizations. This latter case is a particularly difficult challenge because the teams within the project have duties both to the project and to their parent business and enterprise, and must fit into both cultures and process environments.
The detailed topics in this Knowledge Area go into further detail on how a business determines and prioritizes the SE capabilities it needs (Deciding on Desired Systems Engineering Capabilities within Businesses and Enterprises), organizes to do Systems Engineering and integrates SE with its other functions (Organizing Business and Enterprises to Perform Systems Engineering), assesses SE performance (Assessing Systems Engineering Performance of Business and Enterprises), develops and improves its capabilities through organizational learning (Developing Systems Engineering Capabilities within Businesses and Enterprises) and the impact of Culture.
Goals, Measures and Alignment in an Organization
The alignment of goals and measures across the business strongly affects the effectiveness of SE effort and the benefit delivered by SE to the business. For example:
- (Blockley, D. and P. Godfrey. 2000) describes techniques used successfully to deliver a major infrastructure contract on time and within budget, in an industry normally plagued by adversarial behavior.
- Lean thinking (Womack and Jones 2003; Oppenheim et al. 2010) provides a powerful technique for aligning purpose to customer value – provided the enterprise boundary is chosen correctly and considers the whole value stream.
- (Fasser, Y. and Brettner, D. 2002, 18-19) sees an organization as a system, and advocate three principles for organizational design: “increasing value for the ultimate customer”, “strict discipline”, and “simplicity”.
- EIA 632 (EIA 1999) advocates managing all the aspects required for through-life cycle success of each element of the system as an integrated “building block”. Similarly, (Blockley 2010) suggests that taking a holistic view of “a system as a process” allows a more coherent and more successful approach to organization and system design, considering each element both as part of a bigger system of interest and as a “whole system” (a “holon”) in its own right.
- (Elliott et al. 2007) advocates six guiding principles for making systems that work: “debate, define, revise and pursue the purpose”; “think holistic”; "follow a systematic procedure”; "be creative”; "take account of the people”; and “manage the project and the relationships."
- For organizations new to SE, the INCOSE UK Chapter has published a range of one-page guides on the subject, including http://www.incoseonline.org.uk/Documents/zGuides/Z2_Enabling_SE.pdf (Farncombe and Woodcock 2009) and http://www.incoseonline.org.uk/Documents/zGuides/Z3_Why_invest_in_SE.pdf (Farncombe and Woodcock 2009).
References
Works Cited
ANSI/EIA. 2003. Processes for Engineering a System. Philadelphia, PA, USA: American National Standards Institute (ANSI)/Electronic Industries Association (EIA). ANSI/EIA 632‐1998.
Blockley,D. and Godfrey, P. 2000. Doing It Differently – Systems For Rethinking Construction. London, UK: Thomas Telford, Ltd.
Deming, W.E. 1994. The New Economics. Cambridge, MA, USA: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Centre for Advanced Educational Services.
Elliott, C. et al. 2007. Creating Systems That Work – Principles of Engineering Systems for The 21st Century. London, UK: Royal Academy of Engineering. Accessed September 2, 2011. Available at http://www.raeng.org.uk/education/vps/pdf/RAE_Systems_Report.pdf .
Fasser, Y. and D. Brettner. 2002. Management for Quality in High-Technology Enterprises. Hoboken, NJ, USA: John Wiley & Sons-Interscience.
Farncombe, A. and H. Woodcock. 2009. "Enabling Systems Engineering". Z-2 Guide, Issue 2.0. Somerset, UK: INCOSE UK Chapter. March, 2009. Accessed September 2, 2011. Available at http://www.incoseonline.org.uk/Documents/zGuides/Z2_Enabling_SE.pdf.
Farncombe, A. and H. Woodcock 2009. "Why Invest in Systems Engineering". Z-3 Guide, Issue 3.0. Somerset, UK: INCOSE UK Chapter. March 2009. Accessed September 2, 2011. Available at http://www.incoseonline.org.uk/Documents/zGuides/Z3_Why_invest_in_SE.pdf.
Oppenheim, B., E.M. Murman, D.A. Secor. 2010. Lean Enablers for Systems Engineering. Systems Engineering. 14(1): 29-55. Accessed on September 14, 2011. Available at http://cse.lmu.edu/Assets/Lean+Enablers.pdf.
Womack, J. and D. Jones. 2003. Lean Thinking: Banish Waste and Create Wealth in Your Corporation, Revised Edition. New York, NY, USA: Simon & Schuster.
Primary References
Blockley,D. and Godfrey, P. 2000. Doing It Differently – Systems For Rethinking Construction. London, UK: Thomas Telford, Ltd.
Additional References
INCOSE. 2011. Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and Activities, version 3.2.1. San Diego, CA, USA: International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE), INCOSE-TP-2003-002-03.2.1.
ISO/IEC 2008. Systems and Software Engineering -- System Life Cycle Processes. Geneva, Switzerland: International Organisation for Standardisation / International Electrotechnical Commissions. ISO/IEC/IEEE 15288:2008.
SEBoK Discussion
Please provide your comments and feedback on the SEBoK below. You will need to log in to DISQUS using an existing account (e.g. Yahoo, Google, Facebook, Twitter, etc.) or create a DISQUS account. Simply type your comment in the text field below and DISQUS will guide you through the login or registration steps. Feedback will be archived and used for future updates to the SEBoK. If you provided a comment that is no longer listed, that comment has been adjudicated. You can view adjudication for comments submitted prior to SEBoK v. 1.0 at SEBoK Review and Adjudication. Later comments are addressed and changes are summarized in the Letter from the Editor and Acknowledgements and Release History.
If you would like to provide edits on this article, recommend new content, or make comments on the SEBoK as a whole, please see the SEBoK Sandbox.
blog comments powered by Disqus