Difference between revisions of "Enterprise Systems Engineering"
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
===Extended Enterprise=== | ===Extended Enterprise=== | ||
| − | Sometimes it is prudent to consider a broader scope than merely the "boundaries" of the organizations involved in an enterprise. In some cases, it is necessary (and wise) to consider the "extended enterprise" in | + | Sometimes it is prudent to consider a broader scope than merely the "boundaries" of the organizations involved in an enterprise. In some cases, it is necessary (and wise) to consider the "extended enterprise" in modeling, assessment, and decision making. This could include upstream suppliers, downstream consumers, and end [[User (glossary)|user]] organizations, and perhaps even "sidestream" partners and key [[Stakeholder (glossary)|stakeholders]]. The [[Extended Enterprise (glossary)|extended enterprise]] can be defined as: |
<blockquote> | <blockquote> | ||
''Wider organization representing all associated entities - [[Customer (glossary)|customers]], employees, suppliers, distributors, etc. - who directly or indirectly, formally or informally, collaborate in the [[Design (glossary)|design]], development, production, and delivery of a product (or [[Service (glossary)|service]]) to the end user.'' (http://www.businessdictionary.com) | ''Wider organization representing all associated entities - [[Customer (glossary)|customers]], employees, suppliers, distributors, etc. - who directly or indirectly, formally or informally, collaborate in the [[Design (glossary)|design]], development, production, and delivery of a product (or [[Service (glossary)|service]]) to the end user.'' (http://www.businessdictionary.com) | ||
Revision as of 09:13, 13 July 2012
Enterprise systems engineering (ESE) is the application of systems engineering principles, concepts, and methods to the planning, design, improvement, and operation of an enterprise.
To download a PDF of all of Part 4 (including this knowledge area), please click here.
Topics
This series of articles will first provide (1) some background on the scope of ESE, imperatives for enterprise transformation, and potential systems engineering (SE) enablers for the enterprise. It will then discuss (2) how to treat the enterprise as a system and how ESE relates to the concepts of system of systems (SoS) and federation of systems (FoS). Next it will describe (3) related business activities and (4) necessary extensions of TSE concepts that enable these business activities. Each of the ESE process activities is discussed (5) in the overall context of the unique circumstances in the operation of a large and complex enterprise. Finally, it will show (6) how ESE can be used to establish and maintain enterprise operational capabilities. The six topics for this knowledge area are listed below.
- Enterprise Systems Engineering Background
- The Enterprise as a System
- Related Business Activities
- Enterprise Systems Engineering Key Concepts
- Enterprise Systems Engineering Process Activities
- Enterprise Capability Management
Introduction
This knowledge area provides an introduction to systems engineering (SE) at the enterprise level in contrast to “traditional” SE (TSE) (sometimes called “conventional” or “classical” SE) performed in a development project or to “product” engineering (often called product development in the SE literature).
The concept of enterprise was instrumental in the great expansion of world trade in the seventeenth century (see note 1) and again during the Industrial Revolution of the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. The world may be at the cusp of another global revolution enabled by the Information Age and the technologies and cultures of the Internet (see note 2). The discipline of SE now has the unique opportunity of providing the tools and methods for the next round of enterprise transformations.
- Note 1. “The Dutch East India Company… was a chartered company established in 1602, when the States-General of the Netherlands granted it a 21-year monopoly to carry out colonial activities in Asia. It was the first multinational corporation in the world and the first company to issue stock. It was also arguably the world's first mega-corporation, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, negotiate treaties, coin money, and establish colonies.” (emphasis added, http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dutch_East_India_Company)
- Note 2. This new revolution is being enabled by cheap and easily usable technology, global availability of information and knowledge, and increased mobility and adaptability of human capital. The enterprise level of analysis is only feasible now because organizations can work together to form enterprises in a much more fluid manner.
ESE is an emerging discipline that focuses on frameworks, tools, and problem-solving approaches for dealing with the inherent complexities of the enterprise. Furthermore, ESE addresses more than just solving problems; it also deals with the exploitation of opportunities for better ways to achieve the enterprise goals. A good overall description of ESE is provided by in the book by Rebovich and White (2011).
Key Terms
Enterprise
An enterprise consists of a purposeful combination (e.g., a network) of interdependent resources (e.g., people, processes, organizations, supporting technologies, and funding) that interact with
- each other to coordinate functions, share information, allocate funding, create workflows, and make decisions, etc.; and
- their environment(s) to achieve business and operational goals through a complex web of interactions distributed across geography and time (Rebovich and White 2011, 4-35).
The term enterprise has been defined as follows:
(1) One or more organizations sharing a definite mission, goals, and objectives to offer an output such as a product or service. (ISO 15704 2000)
(2) An organization (or cross organizational entity) supporting a defined business scope and mission that includes interdependent resources (people, organizations and technologies) that must coordinate their functions and share information in support of a common mission (or set of related missions). (CIO Council 1999)
(3) The term enterprise can be defined in one of two ways. The first is when the entity being considered is tightly bounded and directed by a single executive function. The second is when organizational boundaries are less well defined and where there may be multiple owners in terms of direction of the resources being employed. The common factor is that both entities exist to achieve specified outcomes. (MOD 2004)
(4) A complex, (adaptive) socio-technical system that comprises interdependent resources of people, processes, information, and technology that must interact with each other and their environment in support of a common mission. (Giachetti 2010)
An enterprise must do two things: (1) develop things within the enterprise to serve as either external offerings or as internal mechanisms to enable achievement of enterprise operations, and (2) transform the enterprise itself so that it can most effectively and efficiently perform its operations and survive in its competitive and constrained environment.
Enterprise vs Organization
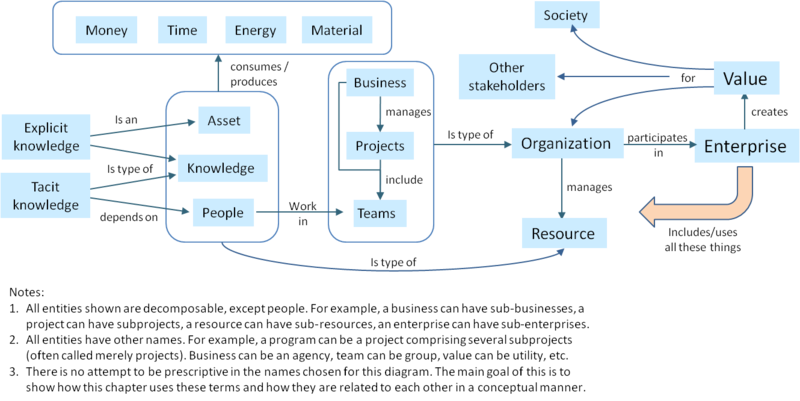
It is worth noting that an enterprise is not equivalent to an "organization” according to the definition above. This is a frequent misuse of the term enterprise. The figure below shows that an enterprise includes not only the organizations that participate in it, but also people, knowledge, and other assets such as processes, principles, policies, practices, doctrine, theories, beliefs, facilities, land, intellectual property, and so on.
Some enterprises are organizations, but not all enterprises are organizations. Likewise, not all organizations are enterprises. Some enterprises have no readily identifiable "organizations" in them. Some enterprises are self-organizing (i.e., not organized by mandate) in that the sentient beings in the enterprise will find for themselves some way in which they can interact to produce greater results than can be done by the individuals alone. Self-organizing enterprises are often more flexible and agile than if they were organized from above (Dyer and Ericksen 2009; Stacey 2006).
One type of enterprise architecture that supports agility is a non-hierarchical organization without a single point of control. Individuals function autonomously, constantly interacting with each other to define the work that needs to be done. Roles and responsibilities are not predetermined but rather emerge from individuals’ self-organizing activities and are constantly in flux. Similarly, projects are generated everywhere in the enterprise, sometimes even from outside affiliates. Key decisions are made collaboratively, on the spot, and on the fly. Because of this, knowledge, power, and intelligence are spread through the enterprise, making it uniquely capable of quickly recovering and adapting to the loss of any key enterprise component. (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Business_agility)
In spite of this lack of "organization" in some enterprises, SE can still contribute much in the engineering of the enterprise, as described in the articles below. However, SE must be prepared to apply some non-traditional approaches in doing so. Hence the need for embracing the new discipline called enterprise systems engineering (ESE).
Giachetti (2010) distinguishes between enterprise and organization by saying that an organization is a view of the enterprise. The organization view defines the structure and relationships of the organizational units, people, and other actors in an enterprise. Using this definition, we would say that all enterprises have some type of organization, whether formal, informal, hierarchical or self-organizing network.
Extended Enterprise
Sometimes it is prudent to consider a broader scope than merely the "boundaries" of the organizations involved in an enterprise. In some cases, it is necessary (and wise) to consider the "extended enterprise" in modeling, assessment, and decision making. This could include upstream suppliers, downstream consumers, and end user organizations, and perhaps even "sidestream" partners and key stakeholders. The extended enterprise can be defined as:
Wider organization representing all associated entities - customers, employees, suppliers, distributors, etc. - who directly or indirectly, formally or informally, collaborate in the design, development, production, and delivery of a product (or service) to the end user. (http://www.businessdictionary.com)
Enterprise SE
Enterprise systems engineering (ESE), for the purpose of this article, is defined as the application of SE principles, concepts, and methods to the planning, design, improvement, and operation of an enterprise (see note 3). To enable more efficient and effective enterprise transformation, the enterprise needs to be looked at “as a system,” rather than merely as a collection of functions connected solely by information systems and shared facilities (Rouse 2009). While a systems perspective is required for dealing with the enterprise, this is rarely the task or responsibility of people who call themselves systems engineers.
- Note 3. This form of systems engineering (i.e., ESE) includes 1) those traditional principles, concepts, and methods that work well in an enterprise environment, plus 2) an evolving set of newer ideas, precepts, and initiatives derived from complexity theory and the behavior of complex systems (such as those observed in nature and human languages).
Creating Value
The primary purpose of an enterprise is to create value for society, other stakeholders, and for the organizations that participate in that enterprise. This is illustrated in Figure 1 that shows all the key elements that contribute to this value creation process.
There are three types of organizations of interest – businesses, projects, and teams (see note 4). A typical business participates in multiple enterprises through its portfolio of projects. Large SE projects can be enterprises in their own right, with participation by many different businesses, and may be organized as a number of sub-projects.
- Note 4. The use of the word “business” is not intended to mean only for-profit commercial ventures. As used here it also includes government agencies and not-for-profit organizations, as well as commercial ventures. Business is the activity of providing goods and services involving financial, commercial, and industrial aspects.
Resource Optimization
A key choice for businesses that conduct SE is to what extent, if at all, they seek to optimize their use of resources – people, knowledge, assets – across teams, projects, and business units. Optimization of resources is not the goal in itself, but rather a means to achieve the goal of maximizing value for the enterprise and its stakeholders. At one extreme in a product-oriented organization, projects may be responsible for hiring, training, and firing their own staff, as well as managing all assets required for their delivery of products or services. (When we say “product-oriented” organization it is not talking about this in the sense of product-oriented SE but rather in the sense of this being one of the basic constructs available when formulating organizational strategy.)
At the other extreme in a functional organization, the projects delegate almost all their work to functional groups. In between these two extremes is a matrix organization that is used to give functional specialists a “home” between project assignments. A full discussion of organizational approaches and situations along with their applicability in enabling SE for the organization is provided in the article called Systems Engineering Organizational Strategy.
The optimization debate can be handled as described in the book called ‘Enterprise Architecture as Strategy’ (Ross, Weill & Robertson 2006). In other words, an enterprise can choose (or not) to unify its operations and can choose (or not) to unify its information base. There are different strategies the enterprise might adopt to achieve and sustain value creation (and how ESE helps an enterprise to choose). This is further addressed in the section on Enterprise Architecture Formulation & Assessment in the article called Enterprise Capability Management.
Enabling SE in the Organization
SE skills, techniques, and resources are relevant to many enterprise functions, and a well-founded SE capability can make a substantial contribution at the enterprise level, as well as the project level. The article called Systems Engineering Organizational Strategy discusses enabling SE in the organization, while the article called Enabling Businesses and Enterprises to Perform Systems Engineering focuses on the cross-organizational functions at the business and enterprise levels. Competence of individuals is discussed in the article called Enabling Individuals to Perform Systems Engineering.
Kinds of Knowledge Used by the Enterprise
Knowledge is a key resource for ESE. There are generally two kinds of knowledge: explicit and tacit. Explicit knowledge can be written down or incorporated in computer codes. Much of the relevant knowledge, however, is “tacit knowledge” that only exists within the heads of people and in the context of relationships that people form with each other (e.g., team, project, and business level knowledge). The ability of an organization to create value is critically dependent on the people it employs, on what they know, how they work together, and how well they are organized and motivated to contribute to the organization’s purpose.
Projects, Programs & Businesses
The term “program” is used in various ways in different domains. In some domains a team can be called a program (e.g., a customer support team is their customer relationship "program"), in others an entire business is called a program (e.g., a wireless communications business unit program), and in others the whole enterprise is called a program (e.g., the Joint Strike Fighter program and the Apollo Space program). And in many cases the terms project and program are used interchangeably with no discernible distinction in their meaning or scope. Typically, but not always, there are program managers who have profit and loss (P&L) responsibility and are the ultimate program decision makers. A program manager may have a portfolio of items (services, products, facilities, intellectual property, etc.) that are usually provided, implemented, or acquired through projects.
The Office of Government Commerce provides a useful distinction between programs and projects:
The ultimate goal of a Programme is to realise outcomes and benefits of strategic relevance. To achieve this a programme is designed as a temporary flexible organisation structure created to coordinate, direct and oversee the implementation of a set of related projects and activities in order to deliver outcomes and benefits related to the organisation’s strategic objectives.
A programme is likely to have a life that spans several years. A Project is usually of shorter duration (a few months perhaps) and will be focussed on the creation of a set of deliverables within agreed cost, time and quality parameters. {OGC 2010}
Practical Considerations
When it comes to performing SE at the enterprise level, there are several good practices to keep in mind (Rebovich and White 2011):
- Set enterprise fitness as the key measure of system success. Leverage game theory and ecology, along with the practices of satisfying and governing the commons.
- Deal with uncertainty and conflict in the enterprise through adaptation: variety, selection, exploration, and experimentation.
- Leverage the practice of layered architectures with loose couplers and the theory of order and chaos in networks.
Enterprise governance involves shaping the political, operational, economic, and technical (POET) landscape. One should not try to control the enterprise like one would in a TSE effort at the project level.
References
Works Cited
CIO Council. 1999. Federal Enterprise Architecture Framework (FEAF). Washington, DC, USA: Chief Information Officer (CIO) Council.
Dyer, L. and Ericksen, J. 2009. "Complexity-based Agile Enterprises: Putting Self-Organizing Emergence to Work." In A. Wilkinson et al (eds.). "The Sage Handbook of Human Resource Management." London, UK: Sage: 436–457.
Giachetti, R. E. 2010. "Design of Enterprise Systems: Theory, Architecture, and Methods." Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group.
ISO 15704. 2000. Industrial Automation Systems -- Requirements for Enterprise-Reference Architectures and Methodologies. Geneva, Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization (ISO), ISO 15704:2000.
MOD. 2004. Ministry of Defence Architecture Framework (MODAF), version 2. London, UK: U.K. Ministry of Defence.
OGC (Office of Government Commerce). 2010. Guidelines for Managing Programmes: Understanding programmes and programme management. London, UK: The Stationery Office.
Rebovich, G., and B. E. White, eds. 2011. "Enterprise Systems Engineering: Advances in the Theory and Practice." Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Auerbach.
Ross, J.W., P. Weill, and D. Robertson. 2006, "Enterprise Architecture As Strategy: Creating a Foundation for Business Execution." Boston, MA, USA: Harvard Business Review Press.
Rouse, W. B. 2009. "Engineering the Enterprise as a System." In "Handbook of Systems Engineering and Management.", eds. A. P. Sage, W. B. Rouse. 2nd ed. New York, NY, USA: Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Stacey, R. 2006. "The Science of Complexity: An Alternative Perspective for Strategic Change Processes." In R. MacIntosh et al (eds.). "Complexity and Organization: Readings and Concersations." London, UK: Routledge: 74–100.
Primary References
Rebovich, G. and B. E. White, eds. 2011. "Enterprise Systems Engineering: Advances in the Theory and Practice." Boca Raton, FL, USA: CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group, Auerbach.
Rouse, W. B. 2005. "Enterprise as Systems: Essential Challenges and Enterprise Transformation." Systems Engineering, the Journal of the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) 8 (2): 138-50.
Rouse, W. B. 2009. "Engineering the Enterprise as a System." In "Handbook of Systems Engineering and Management.", eds. A. P. Sage, W. B. Rouse. 2nd ed. New York, NY, USA: Wiley and Sons, Inc.
Bernus, P., Nemes L., and Schmidt G., eds. 2003. "Handbook on Enterprise Architecture," Berlin & Heidelberg, Germany: Springer-Verlag.
Valerdi, R. and Nightingale, D. J. 2011. "An Introduction to the Journal of Enterprise Transformation," Journal of Enterprise Transformation, 1(1), 1-6, 2011.
Additional References
Drucker, P. F. 1994. "The theory of business." Harvard Business Review (September/October 1994): 95-104.
Fox, M., J. F. Chionglo, and F. G. Fadel. 1993. "A common sense model of the enterprise." Paper presented at the 3rd Industrial Engineering Research Conference, Norcross, GA, USA.
Gøtze, J, ed. Journal of Enterprise Architecture. https://www.aogea.org/journal.
Joannou, P. 2007. "Enterprise, systems, and software—the need for integration." Computer, IEEE, May 2007.
MITRE. 2012. "Enterprise Engineering." In "Systems Engineering Guide." MITRE Corporation. http://www.mitre.org/work/systems_engineering/guide/enterprise_engineering/. Accessed 8 July 2012.
Nightingale, D., and J. Srinivasan. 2011. "Beyond the Lean Revolution: Achieving Successful and Sustainable Enterprise Transformation." New York, NY, USA: AMACOM Press.
Nightingale, D., and R. Valerdi, eds. Journal of Enterprise Transformation. London, UK: Taylor & Francis. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/UJET.
SEBoK Discussion
Please provide your comments and feedback on the SEBoK below. You will need to log in to DISQUS using an existing account (e.g. Yahoo, Google, Facebook, Twitter, etc.) or create a DISQUS account. Simply type your comment in the text field below and DISQUS will guide you through the login or registration steps. Feedback will be archived and used for future updates to the SEBoK. If you provided a comment that is no longer listed, that comment has been adjudicated. You can view adjudication for comments submitted prior to SEBoK v. 1.0 at SEBoK Review and Adjudication. Later comments are addressed and changes are summarized in the Letter from the Editor and Acknowledgements and Release History.
If you would like to provide edits on this article, recommend new content, or make comments on the SEBoK as a whole, please see the SEBoK Sandbox.
blog comments powered by Disqus